By Barbara Nicholson & Lysa Parker, API co-founders, reprinted with permission from Attached at the Heart ©, available through the API Store
 We have been contacted by many parents and caregivers who want to incorporate the most loving behaviors into their feeding practices with their babies. Our culture often supports practices that create disconnection from our children. For instance, some parents have shared with us that they were given baby gear to encourage a “hands off “ style of parenting, including devices to prop a baby bottle so the baby does not have to be held during feedings. An Attachment Parenting International Support Group meeting may be the first place where a parent hears how important it is that babies be fed in the arms of a loved one.
We have been contacted by many parents and caregivers who want to incorporate the most loving behaviors into their feeding practices with their babies. Our culture often supports practices that create disconnection from our children. For instance, some parents have shared with us that they were given baby gear to encourage a “hands off “ style of parenting, including devices to prop a baby bottle so the baby does not have to be held during feedings. An Attachment Parenting International Support Group meeting may be the first place where a parent hears how important it is that babies be fed in the arms of a loved one.
API developed guidelines for bottle-feeding with a unique viewpoint. Because we encourage all parents to look at their parenting choices through the lens of attachment, we have coined the term “bottle nursing” because it reflects breastfeeding behaviors and has tremendous advantages to the parent or other caregiver and baby. These recommendations are applicable to infants who are bottle-fed breast milk, formula, or a combination.
To simulate breastfeeding, parents hold the baby in the crook of the arm, positioning the bottle alongside the breast. This position places the baby’s face and cheek in contact with the parent’s arm, and this skin-to-skin contact helps parent and baby feel more connected. Holding the baby during feeds also helps to prevent the baby from developing “flat-head syndrome,” or plagiocephaly, which can happen when a child is left on a flat surface too frequently. When a baby drinks from a propped bottle, mother and baby also miss an important opportunity to strengthen their emotional connection. Propping the bottle can also be a choking hazard.
Try to make feeding time a special time of calm for both parent and child. Maintain eye contact while feeding when the baby is alert and interested, and switch positions from one side to another; these help strengthen the baby’s eye muscles. Talk softly and lovingly to baby at feeding times. Parents should respect their child’s hunger cues by avoiding feeding schedules. Following the child’s cues helps to strengthen the attachment relationship and shows the baby that his needs are understood.
“We take care of our foster babies as if they were our birth children in every way, except that they are bottle-fed. We hold them as much as we can; I war them in a sling all of the time when I am out in public, and we never take the car seat out of the car. We sleep in close proximity to them; we have a porta-crib next to our bed.
We feed them bottles but use a breastfeeding model, holding them close, never propping the bottle, changing sides for eye-hand coordination, demand-feeding, yet being careful not to overfeed them formula (which is not a concern with breastmilk).
We answer their needs as quickly as is humanly possible, helping them to feel as if they are the most precious beings on this earth.”
~Reedy Hickey, foster mother of 32 infants
Some mothers (or primary caregivers) who bottle nurse choose to follow the breastfeeding model closely so the baby associates feeding with being held; therefore, the mother is the primary person who feeds him while using the bottle. This approach to bottle-feeding produces many benefits for mother and child. The mother will have an opportunity to sit down, to have a special time to bond and rest, just as a breastfeeding mother would be “allowed” to do. A new mother sometimes needs this excuse to rest, instead of feeling that she must do all the housework or other tasks while letting someone else feed the baby. With this behavior, the baby benefits from the consistency of his mother’s presence while feeding and is able to gaze at her face, smell her scent, and feel secure in her arms. This enables their precious attachment relationship to deepen. A mother might say to a well-intentioned relative or friend who wants to feed the baby that this is their special bonding time and a rest time for Mom.
Sucking can remain a strong need well past the first year or two. Pacifiers, when used appropriately, can satisfy that need until the child outgrows it. Breastfeeding babies suck at the breast for comfort, so parents of bottle-fed babies can enrich their child’s experience by either holding the baby in the feeding position when giving a pacifier or simply holding and comforting an older child. These modifications increase close physical contact and bonding time and can make weaning from the pacifier a more natural and gradual process.
As the baby gets older and is able to hold his own bottle, the parent may be tempted to allow the baby to feed himself or to let him walk around with a bottle rather than providing the comfort the child is seeking. If a child doesn’t associate the bottle with being held or having undivided attention by the parent, he might use the bottle or a pacifier as a comfort tool, or “transitional object.” Toddlers who use the bottle, pacifier, or thumb for comfort – rather than being comforted by the parent – may have a much harder time giving up the bottle, pacifier, or thumb down the road. If they learn to come to their parent for comfort or cuddle time and perhaps a short time of sucking on their bottle or pacifier, eventually they will prefer the cuddle and gradually wean from the transitional object, much like a breastfeeding toddler weans from the breast.
In the case of a baby or child who must be separated from their parents during part of the day, it is important that the parent evaluate how important a pacifier or other transitional object is for the security of the child. In some cases, it would be cruel to forbid the use of these comforts, so parents must use their best judgment.
 Five years ago, I had very firm ideas about childhood nutrition. “Balanced meals” was my mantra. I presented plates with foods of different colors (indicating different nutrients), and I sought out whole foods, natural foods, and organic foods. My firstborn stuck up his nose at much of it. Even the foods children are “supposed” to love – macaroni and cheese, pizza, and hot dogs – earned his disdain.
Five years ago, I had very firm ideas about childhood nutrition. “Balanced meals” was my mantra. I presented plates with foods of different colors (indicating different nutrients), and I sought out whole foods, natural foods, and organic foods. My firstborn stuck up his nose at much of it. Even the foods children are “supposed” to love – macaroni and cheese, pizza, and hot dogs – earned his disdain.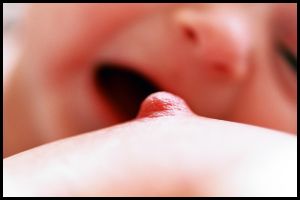
 For many years, I was a guest speaker for the Evergreen Hospital postnatal mom and baby support groups. I would haul a butane burner, pan, some toasted brown rice, a little grinder, and tiny cups to serve samples in up the escalator to the meeting room — I needed luggage with wheels. The room was chock full of moms and babies and toys and blankets, so I had to use my big voice. What I was yelling, while stirring freshly ground rice and water into cereal, was that if I could make this cereal in this room while talking to them, I was sure they could do it at home.
For many years, I was a guest speaker for the Evergreen Hospital postnatal mom and baby support groups. I would haul a butane burner, pan, some toasted brown rice, a little grinder, and tiny cups to serve samples in up the escalator to the meeting room — I needed luggage with wheels. The room was chock full of moms and babies and toys and blankets, so I had to use my big voice. What I was yelling, while stirring freshly ground rice and water into cereal, was that if I could make this cereal in this room while talking to them, I was sure they could do it at home. Nutritional deficiencies in mothers can affect her mental health and lead to inconsistent patterns of mother-child interactions, which in turn increases the likelihood of creating an insecure attachment between the mother and child.
Nutritional deficiencies in mothers can affect her mental health and lead to inconsistent patterns of mother-child interactions, which in turn increases the likelihood of creating an insecure attachment between the mother and child.
 An article on the United Kingdom’s TimesOnline.com, “Tackle Child Obesity: Teach Mums to Eat,” explains how the solution to rising childhood obesity is in teaching parents that their eating behavior is how children themselves learn to eat.
An article on the United Kingdom’s TimesOnline.com, “Tackle Child Obesity: Teach Mums to Eat,” explains how the solution to rising childhood obesity is in teaching parents that their eating behavior is how children themselves learn to eat.

