By Rita Brhel, managing editor and attachment parenting resource leader (API)
 Experts and parents agree – telling and retelling of a birth story is vital for a woman to overcome an emotionally traumatic birth. But there is certainly something to be said for the power of parenting in an attachment-promoting way in healing a mother’s feelings of disappointment, guilt, anger, and other strong and often confusing emotions that may surround her child’s entry into the world.
Experts and parents agree – telling and retelling of a birth story is vital for a woman to overcome an emotionally traumatic birth. But there is certainly something to be said for the power of parenting in an attachment-promoting way in healing a mother’s feelings of disappointment, guilt, anger, and other strong and often confusing emotions that may surround her child’s entry into the world.
Women who are struggling with their emotions are not only grieving their lost dreams of what they had hoped for their labor and birth experience, but may also be battling with feelings of guilt and inadequacy as a mother. While we must take time to fully grieve our birth experiences, we must also find a way to move forward. It can be very fulfilling, and healing, to channel the strong emotions surrounding our child’s birth into caring for her in a loving, positive, attachment-promoting way. Just as a hobby or a phone call to a friend can give a release for our strong emotions in a healthy way, so can we heal through our parenting.
It must be noted, though, that by healing through our parenting, I do not mean that we transfer our strong emotions to our baby or that we attach onto our child in any other way than an appropriate parent-child relationship. What I’m referring to is using parenting as a healthy outlet for women to move forward. Harville Hendrix, PhD, and Helen LaKelly Hunt, PhD, explain this in their book, Giving the Love that Heals.
“In a conscious marriage, partners grow when they stretch to meet the needs of the other, and they heal when their needs are met by their partner,” they write. “The process is mutual. In marriage, it is appropriate for a partner to grow by meeting the needs of the other partner, but it is not appropriate for a parent to try to heal by having the child meet his needs. The process for parents and children is not mutual. The parent must heal his childhood wounds in an adult relationship and not in his relationship with his child.”
However, while healing through the parent-child relationship is not synonymous with the adult-adult relationship, Hendrix and LaKelly Hunt acknowledge that parenting can be a pathway to personal healing.
“The sense in which marriage can be healing is that partners restore their own wholeness when they stretch to meet each other’s needs, giving to the other what is often hardest to give,” they continue. “The sense in which parenting can be healing is that parents restore their own wholeness when they stretch to meet the needs of their children at precisely those stages at which their own development has been incomplete. Through marriage and parenting, partners and parents can recover parts of themselves that have been lost. Both marriage and parenting give people the chance to receive for themselves what they give to their partner or child. They get what they give. In this way, both marriage and parenting can be transformational, because the healing experiences these relationships can provide will change the very character of the people involved.”
Healing from birth trauma is, of course, not the same as healing from childhood wounds, but this excerpt is illustrative of the difference between a parent inappropriately leaning on her baby to provide emotional comfort and a parent appropriately using parenting her baby in an attachment-promoting way as an opportunity to heal through giving to another.
Virtually all Attachment Parenting (AP) practices can help a mother heal from her birth trauma by promoting a close, positive relationship between her and the baby, but there are a few that research has shown to be especially beneficial to the new mother – perhaps not in magically healing emotional trauma but in providing an atmosphere supportive of a mother’s own efforts in healing.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is particularly powerful in jump-starting the mother-baby attachment bond. Attachment Parenting International (API) Co-founders Barbara Nicholson and Lysa Parker describe breastfeeding as the ideal model of attachment in their book, Attached at the Heart, for sale here. There are myriad benefits for the baby and mother, in regards to health and attachment, but what about helping mothers’ emotional well being?
Read API’s review of Attached at the Heart here.
“Breastfeeding triggers the release of the attachment-promoting hormone oxytocin into the mother’s body,” Nicholson and Parker explain. “Often called ‘the mothering hormone,’ oxytocin has a calming effect on both mother and baby. “
Futhermore, “research in depression is showing a correlation between lower levels of certain hormones in mothers who experience depression, so it appears that anything we can do to increase levels of these natural hormones may be a powerful aid in prevention,” Nicholson and Parker write.
Health psychologist and API Resource Advisory Council and API Editorial Review Board member Kathleen Kendall-Tackett echoed this research in her 2007 International Breastfeeding Journal article, “A New Paradigm for Depression in New Mothers: The Central Role of Inflammation and How Breastfeeding and Anti-inflammatory Treatments”: “…although women experience many stressors in the postpartum period, breastfeeding protects them by inducing calm, lessening maternal reactivity to stressors, and increasing nurturing behavior. …breastfeeding can protect mothers’ mental health and is worth preserving whenever possible.”
Responding with Sensitivity & Providing Consistent, Loving Care
Lack of sensitivity toward the baby is a hallmark effect of a mother who is dealing with emotional issues, but a mother who focuses on responding appropriately and quickly to her baby’s cries can improve her mood by reducing how much her baby cries. Nicholson and Parker explain that parents need to respond to their baby’s pre-cry cues; by waiting until the baby is crying, he will be much more difficult to console. Babies are not born with the ability to regulate their strong emotions – they rely on their caregivers to do this for them by responding quickly, appropriately, and consistently.
We don’t need a research study to show us how stressful it can be to listen to our child’s unrelieved cries, but I did want to share one study’s conclusion included in Attached at the Heart. According to a 1995 Pediatrics article, “Developmental Outcome as a Function of the Goodness of Fit Between the Infant’s Cry Characteristics and the Mother’s Perceptions of Her Infant’s Cry,” mothers who responded consistently and appropriately had higher self esteem than did mothers who were inconsistent in the responses to their baby’s cries.
In addition, “mothers who feel low, depressed, anxious, exhausted or angry, who have relationship problems with their partner, or who feel strongly rejected by their baby’s crying are more likely to have a baby who cries excessively,” according to Dr. Gillian Rice in his Netdoctor.co.uk article, “Why Do Babies Cry?” “This isn’t to say that the mother’s feelings caused her baby to become a frequent crier, but they may be a factor in perpetuating the baby’s crying.”
Nurturing Touch
Especially for mothers who are unable to breastfeed, nurturing touch stimulates the mother’s body to also release oxytocin.
“The good news for a mother or caregiver who is not breastfeeding is that she can still receive oxytocin benefits from holding the baby skin-to-skin, and also by giving and receiving nurturing touch through massage and gentle caress,” explain Nicholson and Parker.
Louis Cozolino suggests through his book, The Healthy Aging Brain, that new mothers add nurturing touch as part of their regular infant care techniques, not just for the baby’s benefit but for their own mental health.
“Studies have found that teaching depressed mothers to massage their infants increased the amount of touching and bonding time between them, and decreased levels of stress hormones in both infants and mothers,” he writes. “The infants showed increased alertness, emotionality, and sociability, and they were easier to soothe. Touching their children not only activated smiles and positive expressions on the part of the infants, but also made the mothers feel happier and more effective.”
Cosleeping
I am amazed of how healing it can be at all stages of parenting to sleep in proximity of my children. For the new mother, cosleeping reduces stress and improves sleep by having the reassurance that the baby is nearby and safe as well as the convenience of caring for the baby in the same room rather than in another part of the house.
A study detailed in Sharon Heller’s book, The Vital Touch, describes how “mothers slept slightly better and slightly longer when their babies stayed with them.” Heller goes on to explain how a mother’s instinct is to protect her baby and separation and crying is contrary to this instinct – arousing a mother’s natural impulse to correct the situation.
“From a purely practical standpoint, parents report that they get more sleep with fewer interruptions when the cosleep,” write Nicholson and Parker. “They don’t need to get up to attend to baby’s needs, which keeps parents from having to wake up fully during feedings.”
Cosleeping enhances early mother-baby bonding, because nighttime parenting allows the mother to continue responding with sensitivity around the clock through breastfeeding, nurturing touch, and consistent and loving care.
“Babies feel warm, secure, and protected; therefore, they fret and cry less,” they continue. “Mothers worry less about their infants at night when they can reach out and touch the baby.”
Balance
Striving for balance between our personal and family lives is a must when seeking ways to decrease stress on new mothers and improve mood. Though it may not seem so, AP practices are in many ways just as helpful to maintaining balance in the mother’s life as they are in being compassionate and nurturing to the baby. AP practices aren’t solely for the child’s comfort – mothers receive hormonal benefits through breastfeeding and nurturing touch, more sleep through cosleeping, and reduced stress from crying through responding with sensitivity and providing consistent, loving care.
Still, especially for the first-time mother or for mothers who are going through a difficult postpartum recovery, balance can be an elusive goal. The key is to rely on others for their help in taking care of you. Postpartum Support International names social support as one of the most effective factors in prevention and treatment of postpartum depression. This social support may come in the form of your spouse, mother, friend, local API leader and API Support Group, or even through the virtual connection through the API Forums.
Nicholson and Parker describe the crucial importance of balance in a new mother’s life in Attached at the Heart, warning that “without support and other resources, we are taking a big risk for our children and ourselves. Margot Sunderland addresses the critical issue of stress and balance from a brain chemistry perspective in her power book, The Science of Parenting. She describes the positive effects of the hormone oxytocin and its role in helping calm all human beings. We are designed to help provide emotional regulation for children and each other. When a parent is alone most of the time without other caring adults to talk to, stress hormones rise, feelings get out of balance, and irritability and anger lash out.”
Sunderland’s advice: Mothers need to seek out nurturing touch from their partners, which triggers the release of oxytocin, which then gives a warm, calm feeling. And a sense of balance.
If you’re partner isn’t available or if you’re a single parent, talking to empathic friends can provide a much-needed outlet for stress. Other activities that can give you that oxytocin release include: meditation, acupuncture, massage, physical affection, yoga, warm bath, spending time in the sun or bright artificial lighting.
Discuss this topic with other API members and parents. Get advice for your parenting challenges, and share your tips with others on the API Forum.
 During my second pregnancy, I was a ball of nerves. While my baby was born healthily, she was of a lower birth weight than what was expected – only six pounds for a term baby. My doctor had warned me that not finding a way to lessen my anxiety during the pregnancy could cause problems, and one of those was a low birth weight.
During my second pregnancy, I was a ball of nerves. While my baby was born healthily, she was of a lower birth weight than what was expected – only six pounds for a term baby. My doctor had warned me that not finding a way to lessen my anxiety during the pregnancy could cause problems, and one of those was a low birth weight. Perhaps no activity can consume as much of an expectant couple’s time and energy as choosing a name for their baby. While other aspects of pregnancy and preparing for childbirth and parenting may interest one parent more than the other, both mom and dad are equally invested in the deliberations for just the right name.
Perhaps no activity can consume as much of an expectant couple’s time and energy as choosing a name for their baby. While other aspects of pregnancy and preparing for childbirth and parenting may interest one parent more than the other, both mom and dad are equally invested in the deliberations for just the right name.
 Experts and parents agree – telling and retelling of a birth story is vital for a woman to overcome an emotionally traumatic birth. But there is certainly something to be said for the power of parenting in an attachment-promoting way in healing a mother’s feelings of disappointment, guilt, anger, and other strong and often confusing emotions that may surround her child’s entry into the world.
Experts and parents agree – telling and retelling of a birth story is vital for a woman to overcome an emotionally traumatic birth. But there is certainly something to be said for the power of parenting in an attachment-promoting way in healing a mother’s feelings of disappointment, guilt, anger, and other strong and often confusing emotions that may surround her child’s entry into the world.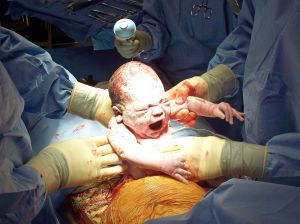 The birth of a child is one of the most significant events in the lives of families. It is considered a rite of passage by many women and involves the first interaction between parents and their baby. There is much buzz today about the necessity of making birth a “family-centered” experience, where the focus is often on creating a special environment for bonding between parents and child in the first moments and days of life. But what if you are one of the women who experiences your baby’s birth as a Cesarean section? Is it possible to make your surgical experience into a family-centered birth?
The birth of a child is one of the most significant events in the lives of families. It is considered a rite of passage by many women and involves the first interaction between parents and their baby. There is much buzz today about the necessity of making birth a “family-centered” experience, where the focus is often on creating a special environment for bonding between parents and child in the first moments and days of life. But what if you are one of the women who experiences your baby’s birth as a Cesarean section? Is it possible to make your surgical experience into a family-centered birth? Family-centered birth is used to describe a birth that is more family oriented, allowing the new family to experience their birth more fully. Many believe that this cannot apply to a surgical procedure. This is not true. Even with a Cesarean surgery, you can have a family-centered birth if you know your options and choose to apply them. Some of the options will be the same as for a vaginal birth. You may have to work harder to have a family-centered birth in the event of surgery, but planning ahead — even if you don’t foresee a Cesarean — can go a long way. Make a birth plan! They won’t know what is important to you unless you let them know, and a birth plan is actually a legal contract as it is providing your wishes in a document provided to your birth team.
Family-centered birth is used to describe a birth that is more family oriented, allowing the new family to experience their birth more fully. Many believe that this cannot apply to a surgical procedure. This is not true. Even with a Cesarean surgery, you can have a family-centered birth if you know your options and choose to apply them. Some of the options will be the same as for a vaginal birth. You may have to work harder to have a family-centered birth in the event of surgery, but planning ahead — even if you don’t foresee a Cesarean — can go a long way. Make a birth plan! They won’t know what is important to you unless you let them know, and a birth plan is actually a legal contract as it is providing your wishes in a document provided to your birth team. Depression is beyond epidemic proportions, not only in the United States but in many societies around the world. People like to blame more recent economic downturns, but these high rates of depression have been an ongoing concern for many years from before the stock markets took a dive.
Depression is beyond epidemic proportions, not only in the United States but in many societies around the world. People like to blame more recent economic downturns, but these high rates of depression have been an ongoing concern for many years from before the stock markets took a dive.
 In preparing the Spring 2009 issue of The Attached Family, I asked a number of women to tell their birth stories who were too uncomfortable in doing so. They were still working through emotions of disappointment, fear, and sometimes guilt surrounding their baby’s birth – even years afterward.
In preparing the Spring 2009 issue of The Attached Family, I asked a number of women to tell their birth stories who were too uncomfortable in doing so. They were still working through emotions of disappointment, fear, and sometimes guilt surrounding their baby’s birth – even years afterward.