By Rita Brhel, managing editor and attachment parenting resource leader (API)
 In an unprecedented move, Attachment Parenting International gathered eight brilliant minds in Attachment Parenting for the organization’s 15th Anniversary Celebration gathering the last weekend of August in Nashville, Tennessee, USA. Never before had all these parenting experts appeared together at an event open to the public. For the hundreds of parents, students, and professionals sitting in the seats of Belmont University’s Troutt Theatre the afternoon of Saturday, August 29, 2009, the “Making an Impact Now: Creating a Sustainable Legacy for Children” Think Tank Event proved truly to be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
In an unprecedented move, Attachment Parenting International gathered eight brilliant minds in Attachment Parenting for the organization’s 15th Anniversary Celebration gathering the last weekend of August in Nashville, Tennessee, USA. Never before had all these parenting experts appeared together at an event open to the public. For the hundreds of parents, students, and professionals sitting in the seats of Belmont University’s Troutt Theatre the afternoon of Saturday, August 29, 2009, the “Making an Impact Now: Creating a Sustainable Legacy for Children” Think Tank Event proved truly to be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
Moderator Lu Hanessian, author of Let the Baby Drive, founder of WYSH, host of API Live! teleseminars, and member of API’s Board of Directors, introduced the panel of speakers, each walking from behind the stage curtain to sit on chairs arranged in a semi circle under a six-foot banner proclaiming API’s anniversary theme: “Growing More Attached.” Making up the panel were:
- Martha Sears, RN – nurse and lactation consultant, La Leche League leader, mother to eight children, co-author of 25 parenting books, and member of API’s Advisory Board and Editorial Review Board.
- William Sears, MD – pediatrician and pediatrics professor at the University of California’s Irvine School of Medicine, father to eight children, and author or co-author to more than 40 parenting books, and member of API’s Advisory Board.
- Ina May Gaskin, MA, CPM – midwife, founder and director of the Farm Midwifery Center in Tennessee, and author of two childbirth books.
- Mary Ann Cahill – co-founder and former director of La Leche League International, mother of nine children, and author of a parenting book.
- Isabelle Fox, PhD – psychotherapist, author of two parenting books, mother, and member of API’s Advisory Board.
- James McKenna, PhD – anthropologist, professor, and director at Notre Dame University’s the Mother-Baby Behavioral Sleep Lab, author of three infant sleep books, and member of API’s Advisory Board.
- Barbara Nicholson, MEd – founder of API, mother to four children, co-author of Attached at the Heart, and member of API’s Board of Directors, Editorial Review Board, and Research Group.
- Lysa Parker, MS, CFLE – founder and former director of API, certified family life educator, mother to two children, co-author of Attached at the Heart, co-leader of API of Huntsville/Madison, and member of API’s Board of Directors, Editorial Review Board, and Research Group.
“This is quite an illustrious panel!” Hanessian said. Special tribute was paid to Nicholson and Parker, for “without you two ladies sitting at the table 15 years ago and commiserating about the future, we would not be here,” Hanessian said before launching into a discussion that could have easily lasted longer than the two hours allotted.
Congratulations, Barbara and Lysa!
Barbara Nicholson and Lysa Parker, API’s co-founders, were surprised during the Think Tank Event with recognition for API’s first Award for Contribution to Parenting going to an AP-minded individual(s) who truly made a difference on parenting. The award was presented by Martha Sears and Dr. William Sears.
Said Dr. Sears of the award recipients: “There are few people – and we really know a lot of people – who I look back on and say, they really made a difference.”
Hanessian opened the Think Tank Event through a series of questions exploring the theme, “Making an Impact Now: Creating a Sustainable Legacy for Children.” To sum it up, she wondered on behalf of parents worldwide what parenting for the future means for the choices parents are making everyday in their homes?
But first, how did API come to be?
API in the Beginning
API, like any effective organization, was borne out a need: “I realized when I had my first child, how few supports there were,” Parker said.
She found new mother support in her local La Leche League, which described a different way of parenting than much of mainstream promoted – one that resonated with her sense of self and where she gravitated toward in her parenting approach. “I think that was a miracle moment for me,” Parker said.
Through the years, Parker and Nicholson saw a need for this parenting approach to get into the reach of more parents. As special education teachers, they encountered children labeled with emotional and behavioral issues and learning disabilities who were, rather, in need of connection with an adult attachment figure. “A lot of problems weren’t really a learning problem but an attachment problem,” Nicholson said.
Read the entire history of API’s founding in the special Attached at the Heart issue of The Attached Family magazine, available at www.attachmentparenting.org/attachedattheheart/journal_aath.pdf.
Ultimately, API came to be as a way to better educate and support attached families, but Attachment Parenting was around long before 15 years ago. Martha Sears and Dr. William Sears, called the Father of Attachment Parenting (AP), coined the term years before API was founded. But the parenting principles that make up AP didn’t start with the Sears.
“In my first year of practice, a wise professor said to me: Surround yourself with very wise mothers,” said Dr. Sears, who is celebrating his 40th year of pediatrics practice this year. “That was my first introduction to Attachment Parenting.”
Empowering Parents
“I worry most about the disempowerment of parents,” said Dr. McKenna.
“We live in a culture of fear,” Hanessian agreed.
API strives to give the power of parenting back to the mother and father, so that they know how to make the best decisions for their children and family despite the sometimes ill-informed and biased advice offered not only by friends and family members but also by medical and other childcare professionals.
“Take back the power,” Parker said. “For far too long, people in the culture have dictated how we should raise our baby, how we should have our baby.”
Gaskin explained how this empowering of parents best happens when advocated for early – at birth. By choosing a midwife, new parents can ensure that the mother and baby can likely be together from labor and delivery forward. By starting as early as possible in keeping parents with their child, their parenting journey pushes forward with connection being considered “normal.”
Parents’ naturally gravitate toward connection, when not influenced by outside forces. What API advocates is for parents to follow that intuition.
“Our fourth child is the one who taught me about intuition,” three decades ago, Martha Sears said, adding that the first three babies were so-called easy babies – or, in other words as McKenna explained, this fourth child would be one of the babies who aren’t as convenient for parents as they wish they would be. This fourth baby required Martha Sears to cosleep in order for her to get some sleep. Although she was following her intuition, it was a scary time for her because the mainstream culture did not support this sleeping arrangement at all. Sears had to learn how to listen to her baby and trust her intuition despite what was popular in parenting advice at the time.
“Thirty years ago! Isn’t that unbelievable that we’re still plagued by that doubt?” Hanessian exclaimed.
What API does is to help parents realize that they are the experts in their child’s care and that, as humans, we are driven toward connection with one another, especially between parent and child. In Western culture, especially, this often means that how they feel toward childrearing doesn’t quite jive with the mainstream advice. API first empowers parents by allowing them the freedom to look beyond mainstream parenting advice to that connection-building that just feels good and right within themselves.
But the key to helping parents pursue this intuitive parenting style is showing the overwhelming research that support AP and API’s Eight Principles of Parenting. Martha Sears agreed, giving an example of the need to show parents the research discrediting cry-it-out sleep training.
Armed with research, API has helped to turn the tide. Parents are now able to find AP resources to support them in their parenting journey. Even in the mainstream culture, more and more experts are saying for parents to listen to their babies.
There are still challenges, though. Western culture is driven by a working population and both parents in most families work outside the home. Dr. Fox recalled a point in her practice when the family dynamic had noticeably changed – when parents were unable to describe the history of their child’s behavioral problems for which Fox had been called to assess and repair, even unable to provide basic childcare facts such as the child’s fears or the potty training technique used. What she found was that the children she most often saw with behavioral issues were those who did not have a consistent caregiver in the early years of life.
That’s why API is so important, Nicholson said – to get these observations, and complementary research, out to parents to show them the long-term effects of nurturing parenting.
This change in parenting practice among the mainstream culture takes time. As Dr. Sears pointed out, parents have been practicing AP for more than 40 years, and while Western culture is incorporating more AP principles into mainstream parenting advice than ever before, AP is still a long ways from widespread acceptance.
Cahill, one of seven women who co-founded La Leche League International 53 years ago, agreed that cultural change does take time. The reason is, parents want to be “good” parents and it can be difficult for a mother or father to sort through the advice they receive from literally every person they encounter, whether the pediatrician, a teacher, a clergyman, a family member or friend, or even by observing what other parents model at the park or grocery store.
“When I had my first baby, I wanted to be the best mother. I wanted to breastfeed,” Cahill said. “And I utterly failed.”
But what she came to realize is that she didn’t fail; instead, society failed her. She didn’t receive any support for breastfeeding. That’s the value of API – a source of support .
Dr. Fox agreed, saying that it’s common for parents to attend childbirth education classes but that they don’t often attend parenting classes until they have a problem they need help with. “Mothers need help with childbirth, but they also need help with [at least] the first year,” she said.
‘Good’ Parenting vs. Good Parenting
That “good” parent myth is also fueled by the voices parents hear in their heads from how their own parents had raised them, Fox said. “We hear our own parents’ voices, and we hear that parent’s voice be critical to us.” Without being aware of the power of those voices, parents will judge how “good” they are by how well they following their own parents’ paths.
“In the beginning, I had to overcome some deficits myself,” Martha Sears explained. Her mother had spanked and practiced other non-AP approaches. She struggled, like many parents must, against that voice in her head that conflicted with her intuition in terms of discipline and communication. In the end – at the point of decision making – all parents either make the choice to do what their parents did with them, or they change through education, support, and often intense emotional work.
Martha Sears said it’s important for parents to keep the future goal in mind: “Remember that you are raising someone else’s future mother or future father. It’s important to get yourself emotionally healthy, so that you can give that gift to your children that keeps on giving.”
Among API’s Eight Principles of Parenting is Preparing for Pregnancy, Birth, and Parenting. Through this principle, API is able to empower people early in their parenting journey – which ultimately makes the challenges of raising children, discipline and communication, easier in the long-term, said Martha Sears. “When you can find a solid way to connect with your children early, you have fewer problems [later],” she said.
“This organization [API] is the only one in existence, except La Leche League, where parents can learn that and that teaches this foundation of attachment,” Martha Sears said.
It can be difficult for parents to sort out their own voice from all the other voices they hear. So, how can parents sort out which voices – whether from their own parents or another outside influence, including API – aligns best with their need for connection with their child?
Today’s Western society is the only culture in history that needs to read a book to know how to parent, said Dr. McKenna. Books are wonderful, but the best teachers are other parents – those experienced in AP. Let’s look at what the expert parents said at the Think Tank Event in response to some of the most confusing areas of parenting.
Discipline
Dr. Bill Sears offered a quick reflective question he learned from his wife, Martha, that parents can ask themselves whenever encountered with a tense situation: “If I were my child, how would I want my mother or father to react?”
“Get behind the eyes of your child. Do you yell, do you spank, do you use sarcasm, do you hug? If you ask yourself that question, and answer truthfully, you’ll always get it right.”
Sleep
Someone, at some point, decided that parenting should shut off at night, said Dr. McKenna. Instead of regarding their baby’s cries as a way of communication, they regarded it a non-communicating noise that the baby makes. What makes crying irritating is when parents fail to see the value in it. A crying baby indicates a need and opportunity for attachment-building.
“Does your baby sleep through the night yet?” is among the most frequently asked questions of the newborn period and can make parents feel guilty if their baby isn’t sleeping through the night – as if they are not “good” parents, Dr. McKenna said.
“Sleep is very relational,” Dr. McKenna said. Crying is natural; it’s a sign that attachment exists, that the baby is seeking the parent out and wants the parent close. Dr. McKenna gave this sample reply for the next time someone asks whether Baby is sleeping through the night yet: “Not only does my baby not sleep through the night, he protests and cries loudly when I’m not there – and isn’t that wonderful? He knows when he’s in danger and isn’t afraid to say so!”
If mainstream society regards a baby who wakes and cries during the night as having a sleep problem, the question is why only half the babies have “sleep problems” and not the full 100 percent, Dr. McKenna said. Why are some of the babies not crying, when crying means there is an attachment bond?
What makes nighttime parenting so difficult is because parents want their sleep and losing sleep is hard. But, “it [parenting] isn’t always going to be easy anyway, because life is like that,” Dr. McKenna said. Even the most informative, well-practiced AP parent can have difficulties in parenting – and infant sleep – if they are caring for a high-needs baby.
Dr. Sears chimed in with a story of a couple who he first saw with their newborn baby and later saw when their baby was three months old. Shorty after birth, the baby was a healthy, happy child and the parents seemed inclined to AP. But, at the three months, the baby wasn’t gaining well and had floppy muscle tone and the parents seemed disconnected.
What had changed? The parents, overwhelmed with their baby’s erratic sleep pattern, had taken a cry-it-out sleep training class. At three months, while the baby was considered “good” in that he slept through the night, the baby’s health was failing in what Dr. Sears refers to as “shut down syndrome” – the baby’s lack of emotional connection with his parents caused him to shut down mentally and physically. It’s a rather common example of the effect that non-AP sleep practices can have on children.
“Beware of baby trainers, because I can tell you, from my practice, it’s a short-term gain by a long-term loss,” Dr. Sears said.
Balance
“This [parenting] is a tough job, and there are a lot of tired moms,” Nicholson said. “What a baby needs is a happy, rested mother.”
Fathers, she said, need to give their wives and partners support – not advice – to ensure that she doesn’t get overwhelmed and is able to find balance between taking care of the child and herself.
But balance is more than self-care; it’s also about healing the emotional wounds left from their own childhoods. “You can’t value someone unless you value yourself,” Dr. McKenna said.
In Utero Bonding
Connection begins even before the baby is born. Nicholson spoke about the importance of parents learning about conscious birth, starting their parenting journey of education and smart choices early. Mothers and babies are not supposed to be separated after birth, Gaskin agreed.
Gaskin recommended that mothers take the time to revel in the baby growing inside them. She suggested mothers focus more on the baby moving and kicking than getting caught up in the technology surrounding pregnancy, such as ultrasounds which unnecessarily distracts some parents.
Consistent and Loving Care
“Babies are ingenious in figuring out who really does what for them,” said Dr. McKenna. Whether this is the mother, father, grandparent, or childcare provider, the baby’s main attachment bond will develop with the primary caregiver. “Our species would not have been successful without significant caregivers,” he added.
That’s why, “what is so important is that mothers have to be there,” said Dr. Fox, who explained that, in all families, one parent should stay at home full-time for the first few years of the child’s life. Often, this is the mother, but more and more, the father is taking on this role in many families. “Fathers can just as well stay home, too,” Dr. McKenna said.
Lately, “fathers are taking more of a role,” Gaskin agreed. “When dads aren’t afraid of babies, I think that’s something very good because that connection is likely to continue.”
Dr. McKenna mentioned the term, “tandem parenting,” in which both the mother and the father share in the care of their child to the point where both are primary attachment figures. This is a new concept, as it has long been thought that a child can only have one primary attachment figure and that the next closest relation would be a secondary attachment figure. The primary attachment preference is based on the father’s behavior toward the baby, not a biological connection.
There is great value in tandem parenting, not only in the benefit to the child who can rely on both parents and to the mother who can take a break here and there, but also to the father himself. When fathers help with their children, their hormone levels fluctuate, Dr. McKenna said. Their oxytocin levels increase and testerone decreases. It’s an actual change in biochemistry.
But, especially with the economic pressures of today’s society, many families are unable to afford one parent to stay at home, so does this mean that they can’t AP? It’s harder for dual-income parents, but certainly possible, Parker said. What they need to do is to focus on reconnecting every day once the parent comes home from work. Hanessian recommended reconnection through cosleeping. Dr. Sears mentioned nursing mothers using breast pumps to be able to continue breastfeeding after they return to work.
“My mother was a single mother juggling two jobs, and what I remember about my mother is that she did the best she could in a less-than-ideal situation,” said Dr. Sears, explaining that while it’s best that a parent is able to stay at home with the children, if it can’t happen, the focus of the parent should be on cultivating that connection as much as possible when together with the child. Children can grow up in situations that are hard but be OK because the memories they have are of happiness and togetherness and connection.
Another way for dual-income parents and single parents is by striving for one, consistent caregiver and being careful about caregiver “roulette,” in which the child’s caregiver is frequently changing. It’s extremely important that a child is able to form a strong, long-lasting primary attachment bond with a caregiver, even if not the parent, and this can only happen with one, consistent caregiver relationship in a childcare situation. Without the formation of a primary attachment bond, as in the case of a child who has many different caregivers, that child will be unable to form healthy attachments and maintain relationships.
Although there are some families who truly cannot afford to have one parent stay at home, Dr. Fox said most families, if they made it a priority, could pull the resources together to do this. More and more jobs are allowing parents to work at home, and the Internet allows parents to more easily start an at-home business, or a family financial budget can help parents adjust to the lifestyle that goes with a lower cost of living.
“You are really needed for the first two years of a baby’s life,” Dr. Fox said. “We go out to borrow money for a house or a car; think about saving that money to stay at home with your baby. It’s not that long.”
What is Good Parenting?
The goal of what mainstream culture considers “good” parenting is how to raise children that won’t embarrass the parents. What API strives to do is to support parents in raising children who grow up connected – that is who are emotionally healthy and able to form strong relationships with others, who want to make good decisions based on their own sense of self and values, and who are empathic and compassionate.
So, how do parents go about doing this?
Dr. Fox explained that AP is based on what is known as the Three Ps:
- Protection – that the child feels protected and cared for.
- Proximity – that the child is physically and emotionally close with the parent.
- Predictability – that the parent is consistent in childcare.
“With protection, proximity, and predictability comes a growing sense of trust and a growing sense of the world’s a pretty good place,” said Dr. Fox.
Dr. McKenna said AP is about parents being conscious of the way they are raising their children. “We tend to think of birth as Independence Day,” he said. “Not that it’s not important, but we’ve overdone it.” Parenting cannot stop at childbirth.
The emphasis placed on childbirth in society needs to spread beyond into childhood; the reason being, babies and children are always developing, always learning. For example, the tastebuds don’t form until the last few weeks of pregnancy, which is why a child tends to like the foods his mother ate during the last part of her pregnancy. And apnea-prone babies can lose up to 70% of their apnea spells by being placed next to teddy bears with a breathing motion. “Every sensory modality that baby has is being regulated by the mother [or father],” said Dr. McKenna.
Dr. Sears said AP is about getting to the basics of relationships in a culture that where the basics can easily be lost in technology. “We’re talking about a low-tech style of parenting in a high-tech world,” Dr. Sears said. He told of a woman in saw in his practice who commented that while she couldn’t afford to buy her son everything that other children had, she could afford to give her son herself.
Dr. Sears also said AP is about parents enjoying parenthood. “Revel in it,” he said.
Highlights from Responses to Audience Questions
Q: Does AP help autistic children?
Nicholson said that in her research, AP was definitely helpful in building connection between an autistic child and his family members .
Dr. Sears said: “If you were to ask me to write a prescription, I’d write ‘Attachment Parenting,’” because autism is a disorder of the brain and Attachment Parenting directly affects the way the brain develops.
Q: How exactly do you form an attachment bond with your child?
Cahill explained that an attachment is established and maintained by the parent meeting the emotional needs of the child. “All the things you’re doing, it creates this parental antennae,” she said and that antennae – or that sense of knowing what your child needs – develops over time.
Q: How can we change the mainstream perspective on cosleeping?
“Never be afraid to say, this is what you do and that you sleep with your baby,” said Dr. McKenna. “We really need to talk, as individuals, about our choices in positive ways.”
Q: How can we deal with the criticism of babies and toddlers not sleeping through the night?
“Here’s the deal: You’re the best sleep expert in your family,” said Dr. McKenna, adding that there are a number of reasons why young children may not be sleeping through the night but the standard that they should be sleeping through the night is unfounded. Every child is different, and comparing one child to another one isn’t effective in evaluating sleep issues.
Q: What does AP look like in an older child?
“If I had to sum up the long-term effect of Attachment Parenting in one word, it would be: empathy – kids who care,” said Dr. Sears. “If I had to sum up the long-term effect of not doing Attachment Parenting: lack of empathy – kids who don’t care.”
Q: Is there an education approach that is more AP than others?
Nicholson, whose children have homeschooled and attended public school and others, said that API does not endorse any particular education option. However, there is an AP way in selection an education option: “Look at each child and see where are their interests and where are they developmentally?” And, if there is only one option and it doesn’t seem to be a good fit for your child, communicate that you share in her frustration and work to problem-solve to make the situation more ideal.
 When I was pregnant for the first time, I wasn’t sure what I would do and I was actually a little afraid of committing to breastfeeding and being my child’s sole source of sustenance.
When I was pregnant for the first time, I wasn’t sure what I would do and I was actually a little afraid of committing to breastfeeding and being my child’s sole source of sustenance. As attachment parents, we need to be sure that we love and accept our children no matter what – and this includes their weight. Some children are naturally, genetically, more overweight or underweight than other children, and this is OK. The reason for the national media attention on children and their weight management is because of the high rates of obesity not only among adults but among children, as well.
As attachment parents, we need to be sure that we love and accept our children no matter what – and this includes their weight. Some children are naturally, genetically, more overweight or underweight than other children, and this is OK. The reason for the national media attention on children and their weight management is because of the high rates of obesity not only among adults but among children, as well. Many women find themselves pregnant while they are still enjoying a nursing relationship with their child. It doesn’t typically occur during the first six months, as long as you and your child are together most of the time and the child is exclusively nursing, but it can happen any time. Your child may be seven months or two years old when you discover you are pregnant. Should pregnancy be the reason to wean? For most mothers, the answer is a resounding no!
Many women find themselves pregnant while they are still enjoying a nursing relationship with their child. It doesn’t typically occur during the first six months, as long as you and your child are together most of the time and the child is exclusively nursing, but it can happen any time. Your child may be seven months or two years old when you discover you are pregnant. Should pregnancy be the reason to wean? For most mothers, the answer is a resounding no!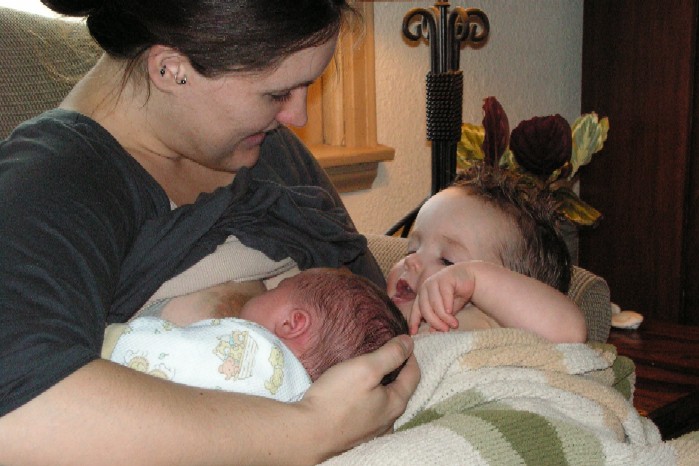 Did you ever think you would be considering nursing two children at the same time? Probably most of us haven’t thought about that, but many women have done it. Known as tandem nursing, it happens all the time with twins and triplets but can be done also be done with children of different ages – for example, nursing your newborn while continuing to nurse your toddler.
Did you ever think you would be considering nursing two children at the same time? Probably most of us haven’t thought about that, but many women have done it. Known as tandem nursing, it happens all the time with twins and triplets but can be done also be done with children of different ages – for example, nursing your newborn while continuing to nurse your toddler. My experience with weaning my daughter was very successful and non-traumatic, which was a good thing since I found it hard to imagine how I would ever refuse her.
My experience with weaning my daughter was very successful and non-traumatic, which was a good thing since I found it hard to imagine how I would ever refuse her. Georgia Jones isn’t accustomed to addressing a crowd as knowledgeable about food as are many attached parents. An University of Nebraska-Lincoln nutrition professor, Jones spends much of her classroom time educating people about the very basics of what they put in their bodies.
Georgia Jones isn’t accustomed to addressing a crowd as knowledgeable about food as are many attached parents. An University of Nebraska-Lincoln nutrition professor, Jones spends much of her classroom time educating people about the very basics of what they put in their bodies. When my sister was a baby, I remember my mom had a food mill at the table and she would feed the same food to my sister that we ate for supper. It seemed easy to me, at four years old.
When my sister was a baby, I remember my mom had a food mill at the table and she would feed the same food to my sister that we ate for supper. It seemed easy to me, at four years old. In an unprecedented move, Attachment Parenting International gathered eight brilliant minds in Attachment Parenting for the organization’s 15th Anniversary Celebration gathering the last weekend of August in Nashville, Tennessee, USA. Never before had all these parenting experts appeared together at an event open to the public. For the hundreds of parents, students, and professionals sitting in the seats of Belmont University’s Troutt Theatre the afternoon of Saturday, August 29, 2009, the “Making an Impact Now: Creating a Sustainable Legacy for Children” Think Tank Event proved truly to be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
In an unprecedented move, Attachment Parenting International gathered eight brilliant minds in Attachment Parenting for the organization’s 15th Anniversary Celebration gathering the last weekend of August in Nashville, Tennessee, USA. Never before had all these parenting experts appeared together at an event open to the public. For the hundreds of parents, students, and professionals sitting in the seats of Belmont University’s Troutt Theatre the afternoon of Saturday, August 29, 2009, the “Making an Impact Now: Creating a Sustainable Legacy for Children” Think Tank Event proved truly to be a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
 I believe it’s that overall style or pattern of action — rather than a specific decision — that will most affect a child’s behavior. Generally, psychologists have found that there are two main components of parenting styles.
I believe it’s that overall style or pattern of action — rather than a specific decision — that will most affect a child’s behavior. Generally, psychologists have found that there are two main components of parenting styles.